Periodontal (gum) diseases, including gingivitis and periodontitis, are serious infections that, left untreated, can lead to tooth loss. The word periodontal literally means "around the tooth." Periodontal disease is a chronic bacterial infection that affects the gums and bone supporting the teeth.
Periodontal disease can affect one tooth or many teeth. It begins when the bacteria in plaque (the sticky, colorless film that constantly forms on your teeth) causes the gums to become inflamed.
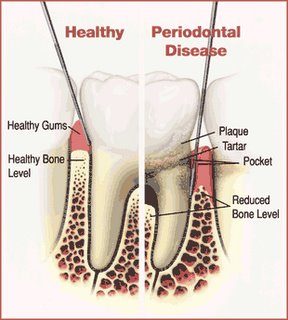
In the mildest form of the disease, gingivitis, the gums redden, swell and bleed easily. There is usually little or no discomfort. Gingivitis is often caused by inadequate oral hygiene. Gingivitis is reversible with professional treatment and good oral home care.
Untreated gingivitis can advance to periodontitis. With time, plaque can spread and grow below the gum line. Toxins produced by the bacteria in plaque irritate the gums. The toxins stimulate a chronic inflammatory response in which the body in essence turns on itself, and the tissues and bone that support the teeth are broken down and destroyed. Gums separate from the teeth, forming pockets (spaces between the teeth and gums) that become infected. As the disease progresses, the pockets deepen and more gum tissue and bone are destroyed. Often, this destructive process has very mild symptoms. Eventually, teeth can become loose and may have to be removed.
Causes of Periodontal DiseaseThe main cause of periodontal disease is bacterial plaque, a sticky, colorless film that constantly forms on your teeth. However, factors like the following also affect the health of your gums.
1.Smoking/Tobacco Use
As you probably already know, tobacco use is linked with many serious illnesses such as cancer, lung disease and heart disease, as well as numerous other health problems. What you may not know is that tobacco users also are at increased risk for periodontal disease. In fact, recent studies have shown that tobacco use may be one of the most significant risk factors in the development and progression of periodontal disease.
2.Genetics
Research proves that up to 30% of the population may be genetically susceptible to gum disease. Despite aggressive oral care habits, these people may be six times more likely to develop periodontal disease. Identifying these people with a genetic test before they even show signs of the disease and getting them into early interventive treatment may help them keep their teeth for a lifetime
3.Pregnancy and Puberty
As a woman, you know that your health needs are unique. You know that brushing and flossing daily, a healthy diet, and regular exercise are all important to help you stay in shape. You also know that at specific times in your life, you need to take extra care of yourself. Times when you mature and change, for example, puberty or menopause, and times when you have special health needs, such as menstruation or pregnancy. During these particular times, your body experiences hormonal changes. These changes can affect many of the tissues in your body, including your gums. Your gums can become sensitive, and at times react strongly to the hormonal fluctuations. This may make you more susceptible to gum disease. Additionally, recent studies suggest that pregnant women with gum disease are seven times more likely to deliver preterm, low birth weight babies.
4.Stress
As you probably already know, stress is linked to many serious conditions such as hypertension, cancer, and numerous other health problems. What you may not know is that stress also is a risk factor for periodontal disease. Research demonstrates that stress can make it more difficult for the body to fight off infection, including periodontal diseases.
5.Medications
Some drugs, such as oral contraceptives, anti-depressants, and certain heart medicines, can affect your oral health. Just as you notify your pharmacist and other health care providers of all medicines you are taking and any changes in your overall health, you should also inform your dental care provider
6.Clenching?Grinding your teeht
7.Diabetes
8.Other systemic disease
No comments:
Post a Comment